Butyl Glycol
CAS: 111-76-2
Butyl glycol also known as BG, 2-butoxyethanol, glycol monobutyl ether and ethylene glycol monobutyl ether is a clear, colourless, oily liquid with a characteristic, but mild, odour with the molecular formula C6H14O2, CAS: 111-76-2. It is miscible with water and with common organic solvents.
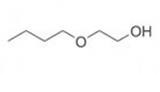
Butyl Glycol Chemical Structure Composition.
Production
Butyl glycol is produced by reacting ethylene oxide and normal butanol (n-butanol) using a catalyst. If the ratio of ethylene oxide to n-butanol is greater than one then di- and tri- ethylene glycol monoethers are also produced.
World production is estimated at between 300-500 KT per annum.
It has a specific gravity of 0.9 and a flash point of 60 °C
Uses
Butyl glycol usage is dominated by the paint industry which consumes approximately 75 % of all the BG produced. This is because it is a low volatility solvent and it can therefore both extend the drying times of coatings and improve their flow.
Other applications include use as a solvent in printing inks and textile dyes and as a component of hydraulic fluids. It is also a component of drilling and cutting oils and is a major component of Corexit 9527, which is an oil spill dispersant product.
It is also a chemical intermediate and, as such, is a starting material in the production of butyl glycol acetate which is, itself, an excellent solvent. It is also a starting material in the production of plasticisers by the reaction of phthalic anhydride. Butyl glycol is also something that is used regularly in most households as it is a component of many home cleaning products. It provides very good cleaning power for domestic cleaning products and also provides the characteristic odour that we associate with many of these products. It also plays the same role in some industrial and commercial surface cleaners.
Arpadis is one of the largest chemical distributor in Europe.
Arpadis is handling the storage, transport, export & import formalities of Butyl Glycol globally.