Ethyl Acrylate
CAS: 140-88-5
Ethyl Acrylate is an acrylate monomer with a molecular formula of C5H8O2, CAS: 140-88-5. It is a clear and volatile liquid with a sharp acrid odour and slightly soluble in water and completely soluble in alcohols, ethers and almost all organic solvents. It is a very flammable liquid with a flashpoint of 9° C.
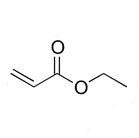
Ethyl Acrylate Chemical Structure Composition.
Production
Ethyl acrylate can be chemically produced using several industrial methods. The most prominent method is to react acrylonitrile and ethanol using sulphuric acid as the catalyst.
Other chemicals used in this reaction are acetylene, carbon monoxide and ethanol.
This product readily polymerizes unless an inhibitor such as hydroquinone is added. Hydroquinone allows to stabilise it during transportation.
Uses
Ethyl Acrylate is primarily used in the production of emulsion-base polymers which can then be used as paints, coatings or latex products. It is mainly used in polyacrylate elastomers, acrylic rubber, textiles, acrylic fibres, leather products. It can be used as a coating on most household items such as books, magazines, plastics, frozen food packaging, fragrance additive, leather, paints, packaging, paper and textiles industries.
Ethyl Acrylate is also a flavouring ingredient that can be used in the food industry for pineapple and passion fruit pulp aroma.
Arpadis is one of the largest chemical distributor in Europe.
Arpadis is handling the storage, transport, export & import formalities of Ethyl Acrylate globally.