Mono Ethylene Glycol – Fibre
CAS :107-21-1
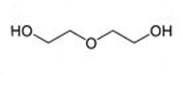
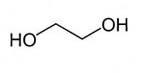
Mono Ethylene Glycol also known as MEG is a clear, colourless, virtually odourless, and slightly viscous liquid. It is miscible with water, alcohols, and many organic compounds, and has the molecular formula C2H6O2, CAS: 107-21-1. It has a specific gravity of 1.115 and a flash point of 110 °C.
Production
Mono Ethylene Glycol is produced by the oxidation of ethylene at a high temperature in the presence of a silver oxide catalyst. The ethylene oxide is then hydrated to yield mono ethylene glycol with di and tri ethylene glycols as co-products.
Uses
Monoethylene glycol (MEG) is an important raw material for industrial applications. MEG is utilized in the manufacture of polyester (PET) resins, films, fibers, antifreezes, coolants, aircraft anti-icer and deicers and solvents.
It is also utilised as raw material for paper industry, polyester Resins, adhesives and inks, chemical Intermediates, Heat Transfer, Fluids.
It is also a used as a dehydration agent in natural gas pipelines where it inhibits the formation of natural gas clathrates.
Arpadis is one of the largest chemical distributor in Europe.
Arpadis is handling the storage, transport, export & import formalities of Mono Ethylene Glycol globally.