Toluene CAS: 108-88-3 Toluene is a clear water-insoluble solvent with a molecular formula of C7H8, CAS: 108-88-3. It has an aromatic, benzene-like smell and is a highly volatile flammable liquid with a flash point of 4° C. It is obtained from petroleum and coal tar. Toluene Chemical Structure Composition. Production Toluene is naturally released into […]

Request a quotation
To request a quotation, please click on the button on the right.
2-Hydroxy-Ethyl Acrylate (2-HEA)
CAS: 818-61-1
2-Hydroxy-Ethyl Acrylate is a Colourless transparent liquid with molecular formula C5H8O3. 2-HEA is readily miscible with water and most organic solvents, alcohol, ether and other organic solvents.
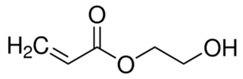
2-Hydroxy-Ethyl Acrylate Chemical Structure Composition.
Production
Ethylene oxide is reacted with acrylic acid to produce hydroxyethyl acrylate.
2-Hydroxyethyl Acrylate (HEA) can be used to impart the following properties to polymers:
- Chemical resistance
- Crosslinking
- Adhesion
- Scratch resistance
- Weatherability
- Rheology modifier
- Low VOC
Uses
2-Hydroxy-Ethyl Acrylate (2-HEA) is mainly used in production of:
- high performance automotive coatings as acrylic enamels where a clear topcoat is applied to increase corrosion protection and durability,
- photocurable acrylic resin,
- polyester-acrylate resins,
- urethane-acrylate,
- emulsion polymers WB ,
- light-sensitive coating,
- Pressure sensitive adhesives (PSA),
- textile treating agent,
- water quality stabilizer,
- high polymer material and as an additive in personal care products and ion exchange resins.
HEA is used mainly either as a co-monomer in the manufacture of polymers and can also be also very useful feedstock for chemical syntheses because it readily undergoes addition reactions with a wide variety of organic and inorganic compounds.
Arpadis is one of the largest chemical distributor in Europe.
Arpadis is handling the storage, transport, export & import formalities of 2-Hydroxy-Ethyl Acrylate globally.


