2-Ethylhexyl Methacrylate (EHMA) CAS: 688-84-6 2-Ethylhexyl Methacrylate is an acrylic monomer with molecular formula C12H22O2 and a molecular weight of 198,3. 2-Ethylhexyl Methacrylate is also known as 2-EHMA; Octyl Methacrylate; Ethylhexyl Methacrylate; 2-Ethylhexyl methacrylate; Ethyl-2-Hexylmethacrylate; 2-Propenoic acid 2-methyl-, 2-ethylhexyl ester; Methacrylic acid 2-ethylhexyl ester; 2-Ethyl-1-hexyl methacrylate. It is a colourless liquid with a ester like […]

Request a quotation
To request a quotation, please click on the button on the right.
Vinyl acetate monomer
CAS: 108-05-4
Vinyl Acetate Monomer also known as VAM, acetic acid ethenyl ester, acetic acid ethylene ether, acetoxyethene, 1-acetoxyethylene, ethenyl ethanoate, ethenyl acetate, and acetic acid vinyl ester with the molecular formula C4H6O2. It is a colourless liquid with a pungent and typical odour.
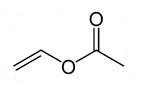
Vinyl Acetate Monomer Chemical Structure Composition.
Production
Vinyl acetate monomer VAM is produced starting from the reaction of ethylene and acetic acid with oxygen. The VAM is recovered by condensation and scrubbing and is purified by distillation.
VAM has a specific gravity of 0.933, a flash point of -8° C and is highly flammable.
Uses
Approximately 75% of all the VAM produced in the world is used to produce polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA).
VAM is a key ingredient in emulsion polymers, resin, and intermediates used in paints, adhesive, coatings, textiles, wire and cable polyethylene compounds, laminated safety glass (PVB), packaging (Ethylene-vinyl acetate EVA), automotive plastic fuel tanks and acrylic fibres.
Polyvinyl acetate is used in paints, adhesives, paper coatings and textile treatments, while polyvinyl alcohol is used in the production of adhesives, coatings, and water soluble packaging, and textile warp sizing.
VAM is also used to make polyvinyl butyral (PVB) which is used in laminated safety glass for cars and buildings.
Arpadis is one of the largest chemical distributor in Europe.
Arpadis is handling the storage, transport, export & import formalities of Vinyl Acetate Monomer globally.


