Polyether amine D2000 CAS: 9046-10-0 Polyether amine D2000 is a member of a family of polyamines having repeat oxypropylene units in the backbone. Polyether amine D2000 is a difunctional primary amine with an average molecular weight of approximately 2000. Its amine groups are located on secondary carbon atoms at the ends of an aliphatic polyether […]

Request a quotation
To request a quotation, please click on the button on the right.
Acrylic Acid
CAS:79-10-7
Glacial Acrylic Acid (GAA) is an unsaturated monocarboxylic acid monomer which is a clear, colourless liquid with an acrid odour which is miscible with water, alcohols and ethers. It’s molecular formula is C3H4O2.
Glacial acrylic acid has useful properties such as flexibility, good weathering, adhesion, hardness and resistance to abrasion and oils and as such it is used as an additive in a wide range of products.
GAA readily copolymerizes with acrylic and methacrylic esters, ethylene, vinyl acetate, styrene, butadiene, acrylonitrile, maleic esters, vinyl chloride and vinylidene chloride.
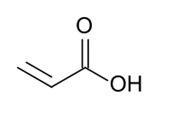
Acrylic Acid Chemical Structure Composition.
Production
Acrylic acid is synthesized by the oxidation of propene via acrolein.
Uses
GAA has two main applications, for the polymeric application and for the manufacture of acrylate esters.
Glacial acrylic acid is commonly used as an additive in a variety of copolymer-based finishes, coatings, adhesives, inks, lubricants, textile, leather, paper finishes, floor polish, plastics, scale inhibitors, hair styling and finishing products, paints, lacquers, plastics, adhesives, dispersants, and thickeners.
It is also used in a range of esters for specialist applications such as in water treatment chemicals when it’s copolymerised with acrylamides, in drilling fluids, in mineral processing chemicals, detergent builders and in super absorbents polymers (SAP) for the production of nappies and sanitary products.
Arpadis is one of the largest chemical distributor in Europe.
Arpadis is handling the storage, transport, export & import formalities of Acrylic Acid globally.


